|
|
Description; structure
- steroids
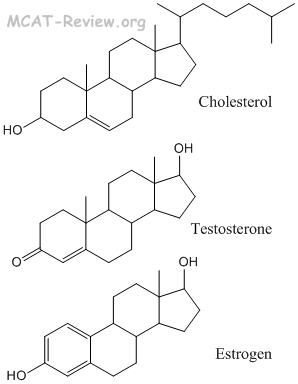
- Steroids are made from the cyclization of squalene, which is a terpene.
- terpenes
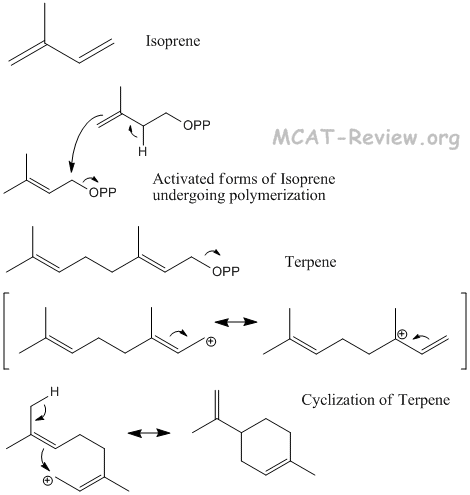
- Terpenes are made from the polymerization of isoprene.
- Terpenes contain double bonds, which gives the molecule the ability to undergo cyclization.
- Squalene, the precursor of steroids, is a terpene that consists of 6 isoprene subunits. A complex self-cyclization reaction converts squalene to make steroids.
- Squalene is classified as a triterpene. Triterpene = 6 isoprene subunits. Diterpene = 4 units. Monoterpene = 2 units.
- triacyl glycerols
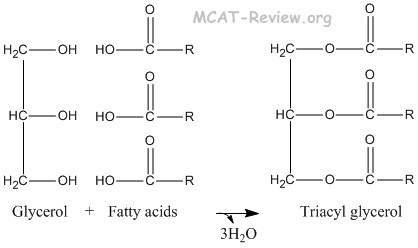
- Glycerol + 3 Fatty acids → Triacyl Glycerol.
- The reverse of triacyl glycerol synthesis is saponification.
- free fatty acids
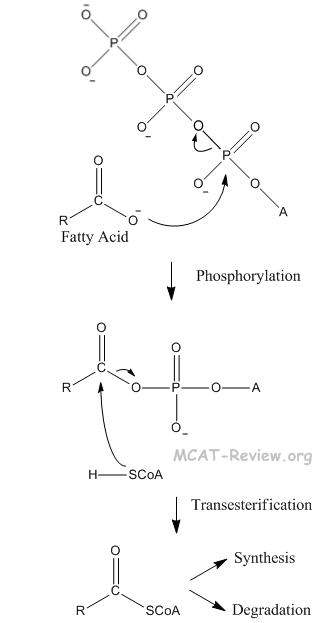
- Fatty acids can undergo phosphorylation and transesterification (commonly called activation by biochemists).
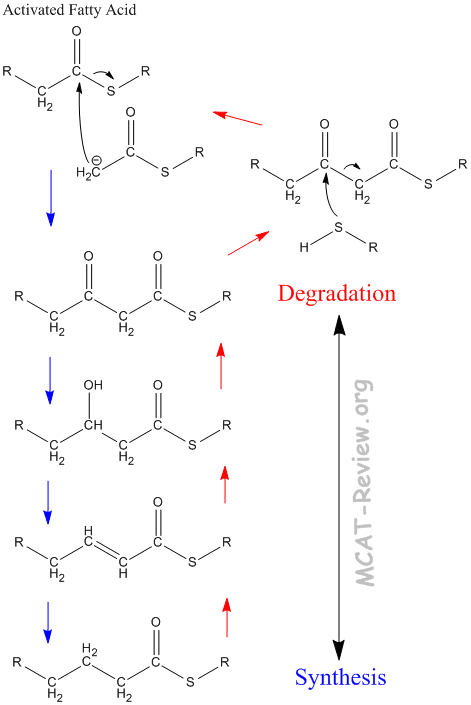
- Fatty acid synthesis occurs via a mechanism similar to the claisen condensation.
|
|
